Let’s explore these concepts in detail, as per Indian Vedic astrology, with examples to make them clearer:
Zonal Standard Time & Time Zone:
- Zonal Standard Time:
- This refers to the standardized time for a specific region, based on its longitude. For example, Indian Standard Time (IST) is set at UTC+5:30, based on the longitude 82.5° East.
- IST ensures uniformity across India, despite the country spanning nearly 30° of longitude.
- Time Zone:
- The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each spanning 15° of longitude. These zones are based on the Earth’s rotation and its relationship with the Sun.
Days, Months, and Years:
- Days:
- A day is divided into 8 praharas (4 for the day and 4 for the night) in Vedic astrology.
- Each prahara spans approximately 3 hours.
- Months:
- A lunar month consists of 30 tithis (lunar days), divided into Shukla Paksha (waxing Moon) and Krishna Paksha (waning Moon).
- A solar month is based on the Sun’s transit through a zodiac sign.
- Years:
- A Vedic year is based on the Sun’s transit through all 12 zodiac signs.
- The Samvatsara system divides time into cycles of 60 years, each with a unique name.
Other Eras:
- Yugas:
- Vedic astrology divides time into four eras: Satya Yuga, Treta Yuga, Dvapara Yuga, and Kali Yuga.
- These eras span millions of years and represent different stages of cosmic evolution.
- Kalpa:
- A Kalpa is a day of Brahma, consisting of 1,000 Maha Yugas (4.32 billion years).
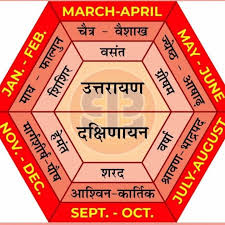
Ayanas:
- Definition:
- An Ayana is a six-month period based on the Sun’s movement. There are two Ayanas:
- Uttarayana: When the Sun moves northward (from Capricorn to Gemini).
- Dakshinayana: When the Sun moves southward (from Cancer to Sagittarius).
- An Ayana is a six-month period based on the Sun’s movement. There are two Ayanas:
- Significance:
- Uttarayana is considered auspicious and associated with growth and prosperity.
- Dakshinayana is associated with introspection and spiritual practices.
These divisions of time reflect the precision and depth of Vedic astrology, connecting celestial movements with human life.