🕰 Local Mean Time (LMT) Explained with India as an Example
Local Mean Time (LMT) is the time based on the longitude of a specific location rather than a standardized time zone. It was widely used before the adoption of standard time zones, especially in astrology and astronomical calculations.
📌 Key Concepts of Local Mean Time (LMT)
- Longitude-Based Time 🗺
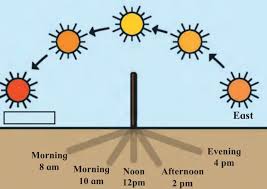
- The Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, meaning each 15° of longitude corresponds to 1 hour of time difference.
- LMT is calculated based on the longitude of a place, which affects sunrise, sunset, and planetary positions.
- Standard Time vs. Local Mean Time
- Standard Time (IST, GMT, EST, etc.) is a fixed time zone used for consistency.
- LMT varies by location and was used before standardization for precise calculations.
🇮🇳 Example: Local Mean Time in India
Before Indian Standard Time (IST = UTC+5:30) was adopted, cities used their own Local Mean Time based on longitude. Here’s how LMT worked:
1️⃣ Kolkata (Longitude: 88.36°E)
- LMT of Kolkata = UTC + 5:53
- Before IST, Kolkata followed its own time, 23 minutes ahead of today’s IST.
2️⃣ Mumbai (Longitude: 72.88°E)
- LMT of Mumbai = UTC + 4:51
- Before IST, Mumbai’s time was 39 minutes behind IST.
🕑 Impact:
- A person born in Kolkata in 1900 would have had their horoscope calculated using Kolkata LMT, not IST.
- Astrologers today adjust historical charts based on LMT corrections.
🔢 Formula to Calculate LMT
LMT = UTC + (Longitude × 4 minutes)
- Each degree of longitude corresponds to 4 minutes of time.
- Example: For Delhi (Longitude: 77.10°E),
LMT = UTC + (77.10 × 4 minutes) = UTC + 5 hours 8 minutes