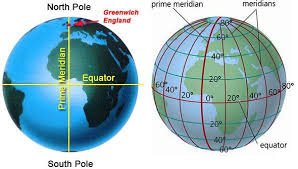
The Prime Meridian is a key reference point in geography and timekeeping. It is an imaginary vertical line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, marking 0° longitude. It helps divide the Earth into Eastern and Western Hemispheres and serves as the starting point for measuring longitude.
Prime Meridian
Why Does the Prime Meridian Matter?
- Longitude Measurement: Every location on Earth has a longitude east or west of the Prime Meridian, up to 180°.
- Time Zones Foundation: Global timekeeping is structured around the Prime Meridian, forming the basis of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- Navigation & Mapping: It provides a fixed reference for charts, maps, and GPS systems.
Real-Life Examples
- Greenwich, England: The Royal Observatory in Greenwich is the official marker of the Prime Meridian (0° longitude).
- Time Zone Calculation: If a city is located at 75° East longitude, it would be 5 hours ahead of GMT (since every 15° represents a 1-hour difference).
- International Date Line: Found at 180° longitude, it sits opposite the Prime Meridian and helps determine where a new day begins.
The Prime Meridian is essential for global coordination, navigation, and time synchronization, forming the backbone of modern timekeeping and mapping.