Here’s a detailed explanation of these concepts related to time difference and geographical coordinates:
Time Differences
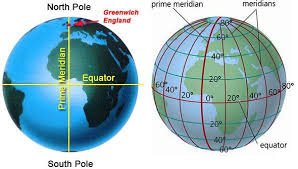
1. Latitude & Longitude
- Latitude refers to the horizontal lines that run parallel to the equator. They measure the distance north or south of the equator in degrees (°).
- Longitude refers to the vertical lines that run from pole to pole. They measure the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
- Together, latitude & longitude help in pinpointing exact locations on Earth.
2. Concept of Prime Meridian
- The Prime Meridian is the 0° longitude, passing through Greenwich, England.
- It serves as the reference point for measuring east-west distances.
- It divides the Earth into Eastern Hemisphere and Western Hemisphere.
3. Time Zones
- The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each covering 15° of longitude.
- As the Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, every 15° shift corresponds to 1-hour difference.
- Countries adjust their time zones based on their longitudinal position.
4. Local Mean Time (LMT)
- Local Mean Time (LMT) is the time calculated based on the longitude of a specific place.
- It is determined by the position of the Sun at noon.
- Every 15° longitude difference results in a 1-hour change in LMT.
5. Standard Time
- Standard Time is the official time used in a country or region.
- Instead of using LMT for every city, countries adopt a single time zone for convenience.
- Example: India follows Indian Standard Time (IST), which is UTC+5:30.
6. Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
- Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Prime Meridian (0° longitude).
- It was historically used as the global reference time.
- GMT is now replaced by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) for precision.
7. LMT Correction
- LMT Correction is the adjustment made to Local Mean Time to align with Standard Time.
- It accounts for the difference between a location’s longitude and the standard meridian of its time zone.
- Example: Delhi’s longitude is 77°E, but IST is based on 82.5°E, so a correction is applied.
These concepts help in understanding time differences, global coordination, and geographical positioning.